HPLC Chiral Analysis and Stereo-Bioactivity of Repaglinide Enantiomers
Keywords:
Repaglinide, HPLC, Chiralcel®OD-RH, molecular docking, antidiabetic, chiral separationAbstract
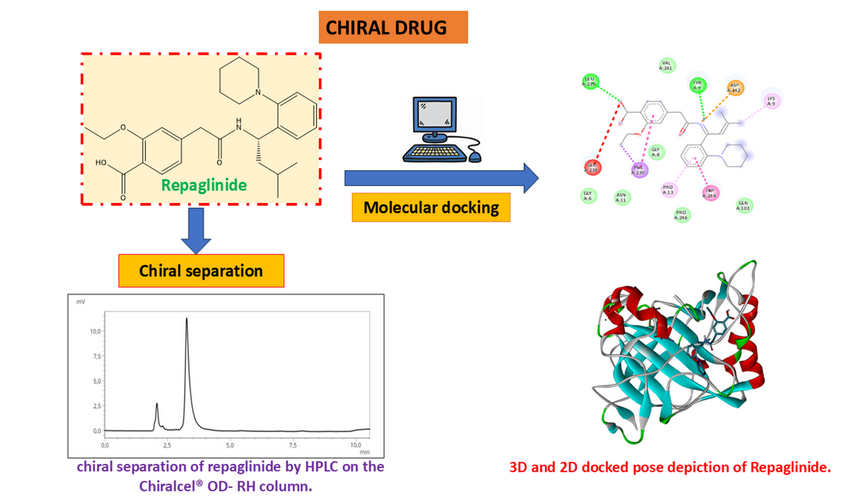
In the present study, a simple, precise and rapid chiral High performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) method has been developed and validated for the enantiomeric separation of Repaglinide, with the molecular docking study of Repaglinide against carbonic anhydrase II (CA2). The method was carried out on a chiralcel® OD-RH column using a mixture of n-hexane: 2-propanol (95:5, v/v), The flow rate was 1.0 ml/min and the eluent was monitored at 240nm. The software used in this molecular docking is PyRx-Virtual Screening Tools (for molecular docking process) and Discovery Studio (for pose visualization and data analysis). According to the study's findings, for HPLC two peaks with a 2.074- and 3,258-min retention time was achieved and the resolution, capacity and selectivity factors obtained were Rs = 0.773; k′1= 1.074, k′2 = 2.258 respectively and α =2,1. The result of molecular docking showed the binding energy of repaglinide to CA2 was found to be -6.8 kcal/mol with RMSD of 1.55 Å, indicating a higher binding affinity compared to native ligand (dansylamide).The method was found to be fast, simple, precise and suitable for analysis of Repaglinide in drug substance.
Downloads
References
J. Penta J, T. Gorre, and N. Reddy Yellu, “Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Interaction Study Of Curcumin With Repaglinide In Normal And Diabetic Rats,” 2017.
J. Yao, Y. Q. Shi, Z. R. Li, and S. H. Jin, “Development of a RP-HPLC method for screening potentially counterfeit anti-diabetic drugs,” J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci, vol. 853, no. 1–2, pp. 254–259, Jun. 2007, doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.03.022.
S. M. Dhole, N. D. Amnerkar, and P. B. Khedekar, “Comparison of UV spectrophotometry and high-performance liquid chromatography methods for the determination of repaglinide in tablets,” Pharm Methods, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 68–72, Jul. 2012, doi: 10.4103/2229-4708.103875.
P. Uppu, N. Kandukoori, N. Yellu “effect of allicin on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repaglinide in normal and streptozocin induced diabetic rats,” Int J Biol Pharm Allied Sci, vol. 10, no. 8, Aug. 2021, doi: 10.31032/ijbpas/2021/10.8.5533.
Sonia K, Nappinnai M, and Manikandan K, “Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Method for the Estimation of Metformin Hydrochloride and Repaglinide as API and Estimation in Tablet Dosage Form,” 2016. [Online]. Available: www.ijpqa.com
R. Aditama, D. Mujahidin, Y. M. Syah, and R. Hertadi, “Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Carbonic Anhydrase II Inhibitors from Phenolic and Flavonoid Group,” Procedia Chem, vol. 16, pp. 357–364, 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.proche.2015.12.064.
B. N. Sağlık et al., “Synthesis, molecular docking analysis and carbonic anhydrase I-II inhibitory evaluation of new sulfonamide derivatives,” Bioorg Chem, vol. 91, Oct. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103153.
M. R. Sharker, Z. P. Sukhan, K. R. Sumi, S. K. Choi, K. S. Choi, and K. H. Kho, “Molecular Characterization of Carbonic Anhydrase II (CA II) and Its Potential Involvement in Regulating Shell Formation in the Pacific Abalone, Haliotis discus hannai,” Front Mol Biosci, vol. 8, May 2021, doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.669235.
M. Jakubowski, E. Szahidewicz-Krupska, and A. Doroszko, “The Human Carbonic Anhydrase II in Platelets: An Underestimated Field of Its Activity,” BioMed Research International, vol. 2018. Hindawi Limited, 2018. doi: 10.1155/2018/4548353.
A. A. El-Zaher, E. F. Elkady, H. H. Elwy, M.A.Saleh “Validated Liquid Chromatographic Method for Simultaneous Determination of Metformin, Pioglitazone, Sitagliptin, Repaglinide, Glibenclamide and Gliclazide - Application for Counterfeit Drug Analysis,” J Anal Bioanal Tech, 2015, doi: 10.4172/2155-9872.s13-007.
J. Zhang, F. Gao, X. Guan, Y. Sun, J. Gu, and J. Paul Fawcett, “Determination of repaglinide in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry,” Acta Pharm Sin B, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 40–45, Jun. 2011, doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2011.04.004.
D. R. Patel, L. J. Patel, and M. M. Patel, “Development and Validation of stability indicating method for the determination of Repaglinide in Pharmaceutical dosage form using High Performance Liquid Chromatography.”
R. Tatiparthi and C. K. Bannoth, “Method development and validation of metformin and repaglinide in rabbit plasma by RP-HPLC,” 2010. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287841113
D. G. Han et al., “Pharmacokinetic evaluation of metabolic drug interactions between repaglinide and celecoxib by a bioanalytical HPLC method for their simultaneous determination with fluorescence detection,” Pharmaceutics, vol. 11, no. 8, Aug. 2019, doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11080382.
P. P. L and N. P. V, “Development and Validation of RP-HPLC Method for the Estimation of Repaglinide in Bulk Drug and Pharmaceutical Formulation.” [Online]. Available: http://www.ijddr.in
M. Abdel Nabi EL-RIES, G. Genidy MOHAMED, and A. Kamal ATTIA, “Electrochemical Determination of the Antidiabetic Drug Repaglinide,” 2008.
A. B. Ruzilawati, M. S. A. Wahab, A. Imran, Z. Ismail, and S. H. Gan, “Method development and validation of repaglinide in human plasma by HPLC and its application in pharmacokinetic studies,” J Pharm Biomed Anal, vol. 43, no. 5, pp. 1831–1835, Apr. 2007, doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2006.12.010.
C. Author, A. Prameela Rani, P. A. Rani, B. C. Sekaran, and S. P. Teja, “Determination of Repaglinide in Pharmaceutical Formulations by RP-HPLC Method,” 2009.
R. Navamanisubramanian, S. Panchagiri, R. Nerella, C. Duraipandian, and S. Seetharaman, “Stability indicating RP-HPLC method for estimation of repaglinide in rabbit plasma,” International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 206–210, May 2019, doi: 10.22159/ijap.2019v11i3.33675.
B. Ramakrishna and S. Mondal, “a review of analytical methods for determination of type-ii antidiabetic drugs in pharmaceuticals and biological matrices,” vol. 14, p. 2021, 2021, doi: 10.22159/ajpcr.2021v14i1.40049.
A. E. Ibrahim et al., “Recent advances in chiral selectors immobilization and chiral mobile phase additives in liquid chromatographic enantio-separations: A review,” Journal of Chromatography A, vol. 1706. Elsevier B.V., Sep. 13, 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2023.464214.
I. Rahou, K. Sekkoum, N. Belboukhari, A. Cheriti, and H. Y. Aboul-Enein, “Liquid chromatographic separation of novel 4-amino-flavanes series diastereomers on a polysaccharide-type chiral stationary phase,” J Chromatogr Sci, vol. 54, no. 10, pp. 1787–1793, 2016, doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmw104.
I. Ali et al., “Determination of enantio-separation, absolute configuration and chiral recognition mechanism of ofloxacin and flumequine by HPLC and modeling studies,” Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, vol. 96, no. 10, pp. 2901–2908, Oct. 2021, doi: 10.1002/jctb.6843.
S. Al-Sulaimi, R. Kushwah, M. Abdullah Alsibani, A. El Jery, M. Aldrdery, and G. A. Ashraf, “Emerging Developments in Separation Techniques and Analysis of Chiral Pharmaceuticals,” Molecules, vol. 28, no. 17. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI), Sep. 01, 2023. doi: 10.3390/molecules28176175.
N. Bounoua, K. Sekkoum, N. Belboukhari, A. Cheriti, and H. Y. Aboul-Enein, “Achiral and chiral separation and analysis of antifungal drugs by HPLC and CE: A comparative study: Mini review,” Journal of Liquid Chromatography and Related Technologies, vol. 39, no. 11. Taylor and Francis Inc., pp. 513–519, Jul. 02, 2016. doi: 10.1080/10826076.2016.1174942.
K. Patil, V. Rane, R. Yeole, and D. Shinde, “A Validated Chiral LC Method for the Enantiomeric Separation of Repaglinide on Immobilized Amylose Based Stationary Phase,” 1048.
V. P. Rane and D. B. Shinde, “A validated chiral LC method for the enantiomeric separation of repaglinide on amylose based stationary phase,” Chromatographia, vol. 66, no. 7–8, pp. 583–587, Oct. 2007, doi: 10.1365/s10337-007-0370-z.
M. Chandra Sharma and S. Sharma, “Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Method for Determination and Validation of Repaglinide in Pharmaceutical Dosage Form.”
A. Raja, “RP- HPLC METHOD DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION FOR SIMULTANEOUS ESTIMATION OF METFORMIN AND REPAGLINIDE IN BULK AND TABLET DOSAGE FORM,” 2015. [Online]. Available: www.uptodateresearchpublication.com
E. N. M. Ho, K. C. H. Yiu, T. S. M. Wan, B. D. Stewart, and K. L. Watkins, “Detection of anti-diabetics in equine plasma and urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry,” in Journal of Chromatography B: Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, Elsevier B.V., Nov. 2004, pp. 65–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.03.070.
M. K. Fayyad and E. H. Ghanem, “Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Determination of Anti-Diabetic Drug Repaglinide in Human Plasma,” Am J Analyt Chem, vol. 05, no. 04, pp. 281–290, 2014, doi: 10.4236/ajac.2014.54035.
P. Naresh, “New RP-HPLC Method for the Estimation of Repaglinide in Bulk and in Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Antioxidant Screening of Some Novel 6-Fluorobenzothiazole Substituted [1, 2, 4] Triazole Analogues View project NOVEL 6-FLUOROBENZOTHIAZOLE SUBSTITUTED [1, 2, 4] TRIAZOLE ANALOGUE View project.” [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334479201
S. S. Aslan and B. Yılmaz, “Derivative Spectrophotometric and Isocratic High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Methods for Simultaneous Determination of Repaglinide and Metformin Hydrochloride in Pharmaceutical Preparations,” Am J Analyt Chem, vol. 08, no. 09, pp. 541–552, 2017, doi: 10.4236/ajac.2017.89039.
K. K. Pradhan, “Method Development, Validation and Stability Study of Repaglinide in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Dosage form by UV Spectrophotometric Method,” 2011. [Online]. Available: www.ijbpr.com
N. S. Abdelhamid, M. T. Elsaady, N. W. Ali, and W. G. Abuelazem, “Simultaneous Determination of Repaglinide, Metformin hydrochloride and Melamine by New HPLC and HPTLC Chromatographic Methods,” Analytical Chemistry Letters, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 418–429, 2019, doi: 10.1080/22297928.2019.1622450.
M. A. Jiladia and S. S. Pandya, “ESTIMATION OF REPAGLINIDE IN BULK AND TABLET DOSAGE FORMS BY HPTLC METHOD.”
S. K. Pawar and S. Jaldappagari, “Interaction of repaglinide with bovine serum albumin: Spectroscopic and molecular docking approaches,” J Pharm Anal, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 274–283, Aug. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2019.03.007.
Fatima. Z. Mimouni, N. Belboukhari, K. Sekkoum, and H. Y. Aboul-Enein, “Novel Gatifloxacin3-Carboxamide Derivatives as Anti-Tumor Agents: Synthesis, Enantioseparation, and Molecular Docking,” Curr Anal Chem, vol. 18, no. 10, pp. 1108–1116, Aug. 2022, doi: 10.2174/1573411018666220819181513.
S. A. Attique et al., “A molecular docking approach to evaluate the pharmacological properties of natural and synthetic treatment candidates for use against hypertension,” Int J Environ Res Public Health, vol. 16, no. 6, Mar. 2019, doi: 10.3390/ijerph16060923.
F. Tajiani, S. Ahmadi, S. Lotfi, P. Kumar, and A. Almasirad, “In-silico activity prediction and docking studies of some flavonol derivatives as anti-prostate cancer agents based on Monte Carlo optimization,” BMC Chem, vol. 17, no. 1, Dec. 2023, doi: 10.1186/s13065-023-00999-y.
“In Silico Pharmacodynamics, Antineoplastic Activity and Molecular Docking of two Phytochemicals Isolated from Thymelaea microphylla.” [Online]. Available: http://www.molinspiration.com/
A. Zamri, N. Frimayanti, and H. Yuda Teruna, “Docking and molecular dynamic simulations: Study of 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole-chalcone hybrid derivatives to search new active anticancer agents.” [Online]. Available: http://www.tjps.pharm.chula.ac.th
I. Rahou, N. Belboukhari, K. Sekkoum, A. Cheriti, and H. Y. Aboul-Enein, “Chiral separation of 4-iminoflavan derivatives on several polysaccharide-based chiral stationary phases by HPLC,” Chromatographia, vol. 77, no. 17–18, pp. 1195–1201, Sep. 2014, doi: 10.1007/s10337-014-2714-9.
G. Widiyarti, Firdayani, M. Hanafi, S. Kosela, and E. Budianto, “Molecular Docking of Citronellol, Geraniol and Ester Derivatives as Pim 1 Kinase Inhibitor of Leukemia Cancer,” Jurnal Kimia Valensi, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 133–142, Nov. 2019, doi: 10.15408/jkv.v5i2.7195.
A. Belal et al., “Design of new captopril mimics as promising ACE inhibitors: ADME, pharmacophore, molecular docking and dynamics simulation with MM-PBSA and PCA calculations,” Journal of Taibah University for Science, vol. 17, no. 1, 2023, doi: 10.1080/16583655.2023.2210348.
N. Rahmadania Hasnaa and R. Trijuliamos Manalu, “Molecular Docking of Turmeric Active Compounds (Curcuma longa L.) against Main Protease in Covid-19 Disease,” East Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (EAJMR), vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 353–364, [Online]. Available: https://journal.formosapublisher.org/index.php/eajmr.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of the Algerian Chemical Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

